Carbohydrates often referred to as carbs, are your body’s primary energy source.
The three main types of carbohydrates are sugars, starches, and fiber. Carbs are sometimes referred to as “simple” versus “complex”. These are also referred to as simple sugars and starches.

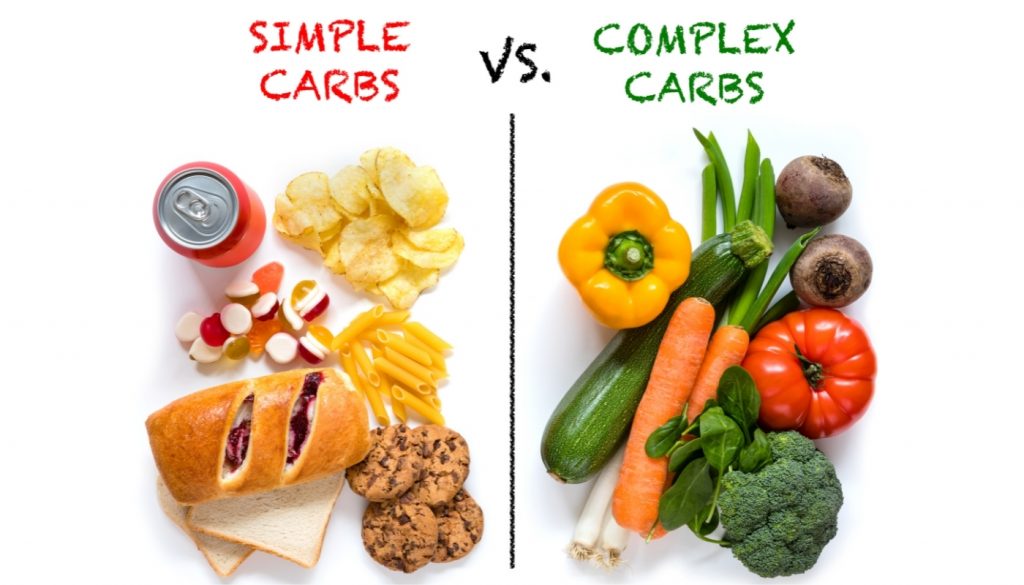
Simple Carbohydrates
Simple carbohydrates are called simple sugars. Sugars are found in a variety of natural food sources including fruit, vegetables and milk, and give food a sweet taste. But they also raise blood glucose levels quickly.
Sugars can be categorised as single sugars (monosaccharides), which include glucose, fructose and galactose, or double sugars (disaccharides), which include sucrose (table sugar), lactose and maltose. People with diabetes will benefit from better blood glucose levels if sugar intake can be limited to lower levels.
For instance, fruits and dairy products contain some simple carbs, but they are drastically different from other foods that contain simple carbs, like cookies and cakes.
Simple carbohydrates to limit or eliminate in your diet include those found in soda, candy, desserts, processed foods such as potato chips, granola bars, and crackers.

Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates, also known as polysaccharides, are starches formed by longer saccharide chains, which means they take longer to break down.
Complex carbohydrates carbs pack in more nutrients than simple carbs. They’re higher in fiber and digest more slowly. This also makes them more filling, which means they’re a good option for weight control.
Complex carbohydrate refers to any starches, including the highly refined starches found in barley, rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, beans, nuts, seeds, most vegetables, and oats, as well as whole grain products like pasta, bread, crackers, etc.
Complex carbohydrates found in whole foods tend to be highly nutritious. For example, whole-grain foods contain a layer of bran and germ, which provide fiber, vitamin B and E, phytochemicals, and healthful fats.

Simple Carbs VS Complex Carbs
Some simple carbohydrates are present in healthful foods, such as milk and whole fruits, that contain a variety of necessary vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients.
Complex carbohydrates contain longer chains of sugar molecules than simple carbohydrates. The body converts these sugar molecules into glucose, which it uses for energy.
As complex carbohydrates have longer chains, they take longer to break down and provide more lasting energy in the body than simple carbohydrates.
Foods with complex carbohydrates also typically have more important nutrients, including fiber and B vitamins, than foods containing more simple carbohydrates, as long as you’re choosing whole grains over processed ones.
In general, 45-65% of your caloric intake should come from carbs, most of which should be complex carbs. If you can limit the amount of refined foods you eat and focus on consuming mostly whole grains and other foods from the complex carb examples above, you’ll garner greater nutrient value and assure a steady flow of energy to fuel your athletic activities and everyday adventures.